
It is recommended to use or create a wireshark profile specifically for analyzing wireless packet captures. The filtering of wireless packets is different as compared to wired filters on wireshark. The sections below investigate those frames with the help of packet capture given above. The management, control, and data frames.
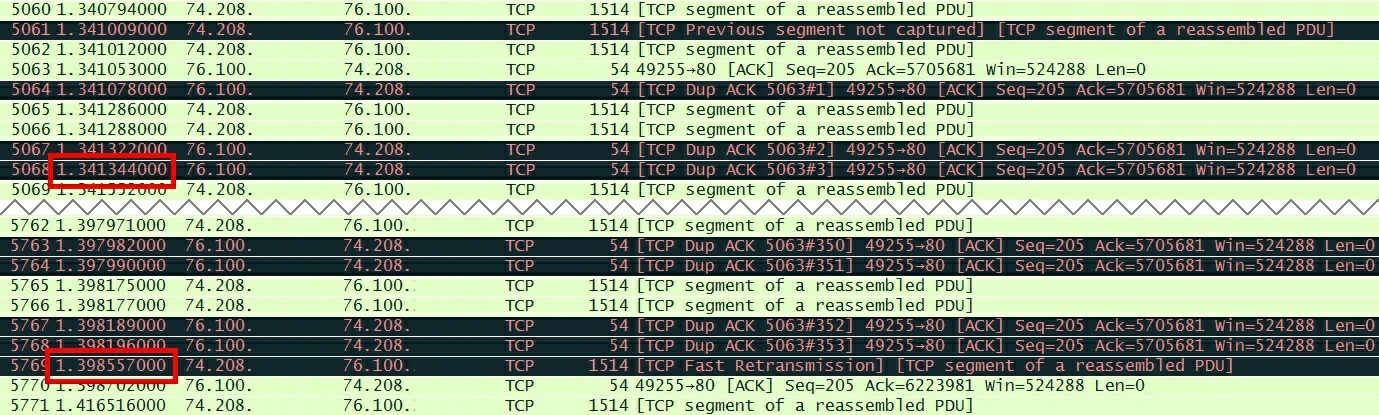
Constant tcp retransmission wireshark mac#
The display filter used was "wlan.addr = 00:21:6b:f7:3a:d2 and (wlan.fc.type = 0x00 or eapol)"Īs mentioned above in the 802.11 packet structure section, there are 3 types of frames used in 802.11 MAC layer communications happening over the air which manage and control the wireless link. The packet capture is shown here in Wireshark. Here is an example of a complete client authentication process from the above packet capture. The client is now able to pass traffic to the access point.The access point will reply with an association response with a success message, granting network access to the client.Upon successful authentication, the client sends an association request frame to the access point.The access point sends an authentication reply, inviting the client to authenticate to the SSID.The client decides which AP is the best for access (based on compatibility with received probe responses) and sends an authentication request to the AP it deems best to connect to.Access points within range respond with a probe response frame, advertising the SSID (wireless network name), supported data rates, encryption types if required, and other 802.11 capabilities of the AP.

The client broadcasts probe request frames on every channel, to all APs. Probe requests advertise the mobile stations supported data rates and 802.11 capabilities such as 802.11n.Access points (APs) continuously send out beacon frames which are picked up by nearby WLAN clients, advertising their SSIDs and data rates.Maximum signal strength, you are probably standing right next to the access point.īased on 802.11 specifications, the client authentication process consists of the following:
Reliable signal strength– the edge of what Cisco considers to be adequate to support Voice over WLANĪnything down to this level can be considered excellent signal strength. This information is useful for determining the expected quality of the signalĬhances of connecting are very low at this level


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
